Quick Summary: AngularJS and Angular development frameworks remain the leading frameworks for application development. When considering the angular and angularjs difference, it's important to note that Angular significantly outperforms AngularJS, and migrating to Angular is crucial for building modern, high-performance applications. But to decide which one to use for your upcoming projects requires an in-depth understanding of Angular vs AngularJS.
Introduction
Choosing the right front-end framework has never been more important. With web apps becoming richer, faster, and more interactive, it’s no surprise that Angular powers over 1.8 million websites today, including Google Cloud Console, Gmail, Forbes, Upwork, and more.
But at the same time, many businesses still rely on older applications built with AngularJS, which naturally brings up the long-running question: What’s the real difference between Angular and AngularJS, and which one makes sense for your project today?
Whether you are optimizing an existing product, planning a migration, or choosing a framework for a new build, understanding Angular vs AngularJS helps you make a decision that impacts performance, scalability, security, and long-term viability.
In this blog, we break down the key differences in a clear, updated, and practical way, so you can confidently choose the right path forward.
Major Difference between Angular and AngularJS (Angular Vs AngularJS)
The main difference between Angular and AngularJS is that Angular is a complete rewrite of AngularJS based on Typescript, offering improved performance and a component-based architecture, whereas AngularJS relies on plain JavaScript and a directive-based approach. The differences between Angular and AngularJS include their underlying architecture, performance capabilities, and modern tooling support. You can compare Angular and AngularJS to see how each framework has evolved and which is more suitable for current web development needs.
The general consideration of these frameworks for your business needs would be determined by your goals and expectations for that project.
Key Takeaways
- Angular is based on Typescript and uses a component-based structure, while AngularJS uses JavaScript and an MVC pattern.
- The differences between Angular and AngularJS impact performance, scalability, and tooling.
- When you compare Angular and AngularJS, consider their evolution and relevance for modern applications.
Let's look at this article to learn the difference between Angular and AngularJS or Angular vs AngularJS, along with their concepts.
Let's start with an in-depth overview of Angular, its features, and pros vs. cons.
Overview of Angular
Angular is an open-source web framework that is entirely free to use. It was developed by Google and released in September 2016 for public use. Although it is considered a Javascript-based framework, its primary programming language is TypeScript. An angular application is built using the Angular framework and TypeScript, featuring a component-based structure that enables modular development.
Since its initial release in 2016, Angular has seen several major updates, with new angular framework versions introducing enhanced features and improvements. Notable versions include Angular 14 and Angular 19, each bringing advancements in performance, tooling, and developer experience.
Developed by Microsoft, TypeScript is a superset of JavaScript, which means that TypeScript has all the capabilities JS has, plus some additional features.
When Google released Angular (2+) in 2016, it was a complete re-engineering of AngularJS to overcome its limitations. Built on TypeScript, equipped with a component-based architecture, and optimized for speed, scalability, and enterprise-grade applications, Angular quickly became a go-to framework for modern web development.
Today, its relevance is stronger than ever. According to the Stack Overflow Developer Survey, over 20% of professional developers use Angular, keeping it among the top web frameworks globally.
Angular evolves continuously through scheduled major releases, bringing performance upgrades, better developer experience, and long-term support, something enterprises value deeply.
Features of Angular
- Cross-Platform: The angular cross-framework platform enables you to create stunning UIs for web and native mobile and desktop applications. Also, the framework is convenient for developing macOS, Windows, and Linux operating systems applications.
- Makes Use of TypeScript: Angular uses the programming language TypeScript, ensuring fewer errors during the compile time as the types of variables are defined beforehand. Also, any piece of JavaScript code is valid TypeScript code.
- Angular CLI (Command Line Interface): This feature lets you speed up the development process. From setting up the project to adding components, there are multiple tasks that you can carry out by simply using Angular’s native CLI.
- Unit Testing Support: With Angular, it becomes feasible to execute unit testing hassle-free and, thus, ensure that your code has minimal bugs.
- Dependency Injection Feature: Angular's dependency injection feature allows efficient management of dependencies for components and services, enhancing modularity and code reusability by enabling services like data fetching and validation to be injected into multiple components.
- Data Binding Feature: Angular provides a powerful data binding feature that synchronizes the model and view, improving performance and responsiveness. It supports different types of data binding, such as one-way and two-way, to suit various application needs.
- One Way Data Binding: By default, Angular uses one way data binding, which optimizes performance by reducing unnecessary DOM updates and limiting data flow to a single direction, while still allowing two-way binding when needed via ngModel.
- Component-Based Architecture: Applications are built using reusable, self-contained components, making Angular apps easier to maintain, test, and scale.
- Modular Structure: Angular apps can be broken into feature modules, enabling efficient code organization and lazy loading.
- RxJS for Reactive Programming: Angular embraces observables, making asynchronous operations more predictable and powerful.
- Ahead-of-Time (AOT) Compilation: Compiles HTML and TypeScript during build time, improving load speed and runtime performance.
Pros
- Highly structured and ideal for large-scale, enterprise-level applications
- Strong performance due to AOT compilation and change detection improvements
- Backed by Google with regular updates and long-term support
- Rich ecosystem including Angular Material, RxJS, and CLI
- Better maintainability thanks to TypeScript and a modular architecture
Cons
- Steeper learning curve, especially for beginners
- Heavier framework size compared to lightweight alternatives like Vue
- Frequent major updates can require periodic refactoring
Overview of AngularJS
Angular JS is a legacy version of the Angular framework that is also an open-source JavaScript framework suitable for front-end web development. This trending framework has a broad scope for structuring exceptional single-page web apps. In AngularJS's architecture, the MVC acts as the central component responsible for managing data, logic, and application behavior, forming the core structure around which the app's functionality is built.
This framework builds templates using HTML. AngularJS controllers and directives interact with the document object model (DOM) to define behavior and add functionality to web page elements. It is popular and demanding in the developer community because of its scalability and natural intuitiveness. Simply put, when a programmer builds a Single-page application with AngularJS, the page loads quickly, delivering an excellent user experience and much easier to maintain. AngularJS was historically used to build performant web applications due to its architecture and features that optimized development speed, maintainability, and user experience.
“Do you know: there are more than 6 billion websites built with Angular JS around the globe as of 2025, and the number is rising sharply?”
AngularJS Features
Below are the highlights of AngularJS features.
- Use of Plain JavaScript: AngularJS framework uses plain JavaScript programming language, which implies that the models in AngularJS are plain JavaScript objects. This feature makes it easy to test and maintain the code created with AngularJS.
- Controllers and Directives: The directive and controllers in AngularJS allow you to choose the functionality and have complete control over the application behavior.
- Reusable Components: With AngularJS, you can develop reusable elements that you can employ multiple times within an application. To create these components, you need to make use of directives. A component can define a particular functionality.
- Dependency Injections: AngularJS uses dependency injections to enhance modularity, readability, and reusability. This feature allows objects to depend on services without managing their construction, making the architecture more flexible and maintainable.
- Routing: Routing is the feature that enables you to switch between different views of an application. Simply put, routing allows users to navigate via different pages of a website or various sections of a web app.
- Two-Way Data Binding: Changes in the UI immediately reflect in the model and vice versa. In the early 2010s, this dramatically reduced boilerplate code.
- MVC/MVVM Architecture: AngularJS introduced a structured way to organize code, using controllers, scopes, and views.
- Directives: AngularJS allowed developers to extend HTML with custom attributes like ng-repeat, ng-model, etc., a powerful concept at the time.
Recommended Read: Top 10 AngularJs Features You Should Know
Pros and Cons of AngularJS
Below are a few pros and cons of the Angular JS development framework.
Pros of AngularJS
- AngularJS enables developers to develop applications with dynamic and responsive user interfaces, thanks to its powerful data binding techniques.
- It supports two-way data binding, which simplifies the synchronization between the model and the view.
- The framework offers reusable components, making code maintenance easier.
- Dependency injection in AngularJS improves testability and code organization.
- Two-way binding and built-in directives reduce repetitive code.
- Has a strong early community & enterprise adoption
Cons of AngularJS
- Scaling Challenges: As apps grow, two-way binding and the digest cycle can slow down performance.
- Not Ideal for Large, Complex Applications: Architecture becomes harder to manage compared to modern component-based frameworks.
- Limited Modern Tooling: No built-in TypeScript, CLI, or advanced debugging tools that modern Angular offers.
- Outdated for New Development: While still in use, AngularJS lacks the speed, security updates, and long-term ecosystem support needed for new projects.
- Harder to Optimize for Mobile: AngularJS apps can struggle with performance on mobile devices due to older rendering patterns.
Building Angular Applications
Building dynamic web applications with Angular is streamlined and efficient, thanks to the framework’s comprehensive solution for developing single page applications. Angular’s component-based architecture allows developers to create reusable components, making it easier to manage and scale complex web applications. The powerful dependency injection system simplifies the management of services and dependencies, promoting cleaner and more maintainable code.
One of the standout features of the Angular framework is its two-way data binding, which ensures that changes in the user interface are instantly reflected in the underlying data model and vice versa. This improved data binding, combined with Angular’s advanced change detection mechanisms, results in responsive and interactive user experiences.
Developers can take advantage of the Angular CLI (Command Line Interface) to quickly scaffold new projects, generate Angular components, and automate tasks such as unit testing and building for production. The CLI tool supports both JavaScript and TypeScript, giving teams flexibility in their choice of programming language.
Angular’s hierarchical dependency injection system and support for lazy loading enable the development of high performance web applications by optimizing resource usage and loading only the necessary modules when required. These features, along with robust unit testing capabilities, make Angular a preferred choice for building dynamic, scalable, and maintainable web applications.
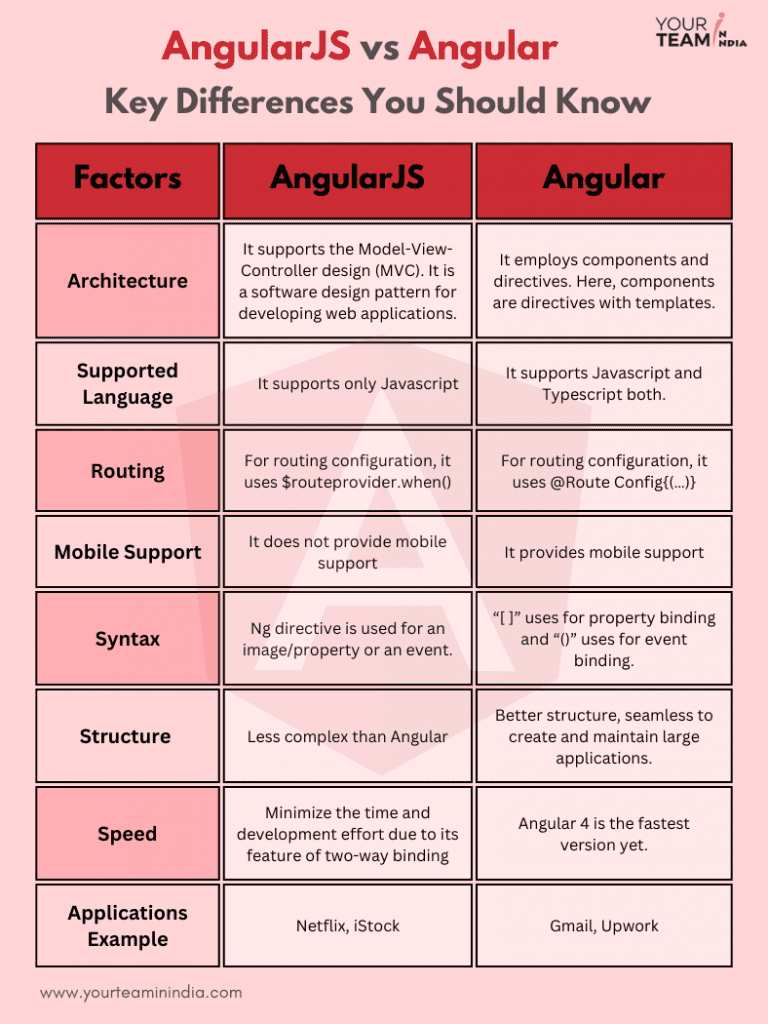
Key Differences between Angular vs Angularjs
Let’s briefly overview the difference between Angular and AngularJS.

|
Parameters |
AngularJS |
Angular (2-latest) |
|
Architecture |
MVC / directive-based |
Component-based, modules, reactive architecture |
|
Language / Typing |
JavaScript (dynamic) |
TypeScript (static typing), optional JavaScript / ESNext, better tooling |
|
Routing |
For routing configuration, it uses $routeprovider.when() |
For routing configuration, it uses @Route Config{(…)} |
|
Performance & Rendering |
Two-way binding with digest cycle (slower for large apps) |
Optimized change detection, tree-shaking, AOT compilation, lazy loading, faster & scalable |
|
Data Binding |
Mainly two-way binding (), easier but leads to performance issues at scale |
Primary one-way or reactive; two-way possible via [(ngModel)], but the default is optimized unidirectional flow |
|
Syntax |
Ng directive is used for an image/property or an event. |
“[ ]” uses for property binding and “()” uses for event binding. |
|
Structure |
Less complex than Angular |
Better structure, seamless to create and maintain large applications. |
|
Dependency Injection |
Basic DI, less modular |
Hierarchical DI, better modularity, testability, service reuse |
|
Tooling & Ecosystem |
Older ecosystem; fewer modern tools |
Rich ecosystem: Angular CLI, support for RxJS, tooling support, large community, frequent updates |
|
Mobile / Cross-Platform / PWA / SSR / SEO |
Limited; no built-in SSR / PWA support |
Supports modern web paradigms: PWA friendly, SSR via Angular Universal (helps SEO), mobile-responsive, easier integration with mobile wrappers / hybrid apps, plus third-party support for native/hybrid apps |
|
Maintainability / Scalability |
Less modular, harder to maintain as app grows |
Highly modular, easier to scale, maintain, refactor, suitable for large enterprise-scale apps |
|
Community & Support |
Legacy; less active, fewer updates (AngularJS is effectively legacy) |
Active development, frequent releases, large community, strong documentation & support |
Since now we are done with the quick glance, below is a more descriptive, simplified comparison across the parameters that matter most.
Architecture & Design
AngularJS follows the MVC (Model–View–Controller) pattern. It’s easy to start with, but as the application grows, managing controllers, scopes, and templates becomes harder. The architecture wasn’t designed with large-scale enterprise apps in mind.
Angular, on the other hand, uses a component-based architecture, where each UI part has its own logic, template, and styling bundled together.
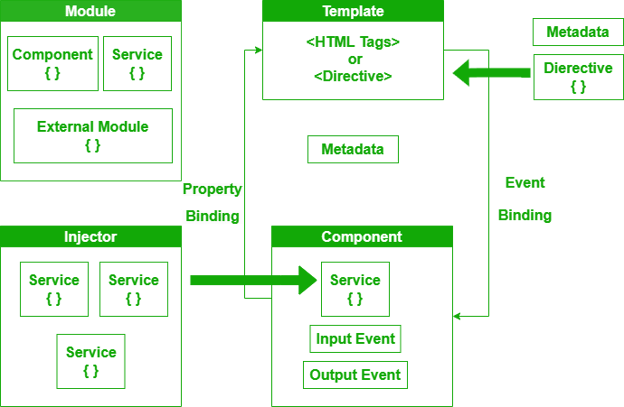
This makes Angular far more suitable for modular development, reusable components, clean folder structures, and long-term scalability. Ideal for complex web apps used by enterprises.
Language & Typing
AngularJS is written in JavaScript. Developers get flexibility, but also more chances for bugs, inconsistent data types, and runtime errors.
While Angular is built on TypeScript, which adds static typing, interfaces, decorators, and advanced tooling. This gives developers better error detection, easier debugging, predictable code, and an overall cleaner development experience.
Performance & Rendering
AngularJS runs on a digest cycle, which constantly checks every data binding in the app. This becomes slower as the app grows, making performance difficult to scale.
Angular uses AOT (Ahead-of-Time) compilation, tree shaking, and the Ivy renderer. This leads to faster load times, smoother rendering, and much better performance even for large and complex applications.
Data Binding & Change Detection
AngularJS follows two-way data binding and is automatic. While it helps you build UI fast, it creates hidden dependencies between components and increases performance overhead.
Angular offers one-way data flow by default, plus an optional two-way binding. This improves predictability, makes debugging easier, and ensures the app doesn’t slow down due to excessive bindings. Angular’s change detection is also more optimized and predictable.
Dependency Injection & Modularity
AngularJS has a Dependency Injection (DI) system, but it's basic and can feel rigid in larger applications. Managing dependencies across modules is not always straightforward.
Angular comes with a powerful hierarchical DI system and NgModules for organizing code. Features like lazy loading, service providers, and modular structure make Angular significantly more scalable and better suited for enterprise development.
Tooling, Ecosystem & Community Support
AngularJS has a limited tooling, older libraries, and declining community activity. Most modern libraries no longer support AngularJS.
Angular ships with Angular CLI for instant scaffolding, boilerplate generation, testing, and builds. It is supported by a strong ecosystem, including Angular Material, RxJS, Universal, and more. It is backed by Google with frequent releases and active community support.
Mobile, PWA, SSR & Cross-Platform Capabilities
AngularJS is not optimized for mobile. It has no built-in support for PWAs or SSR. In fact, developers often rely on workarounds.
Angular is designed with mobile and cross-platform compatibility in mind. It supports:
- PWAs out of the box
- Server-Side Rendering (SSR) through Angular Universal
- Hybrid mobile apps via Ionic
- Native apps through NativeScript
This makes Angular a complete ecosystem for multi-device experiences.
Maintainability, Scalability & Long-Term Viability
AngularJS is great for legacy apps or small tools, but challenging to scale. Since it’s no longer actively updated, long-term app maintenance becomes costly.
Angular is built for longevity. Its modern architecture, strong TypeScript foundation, regular updates, and flexible tooling ensure long-term maintainability and smooth scalability, especially for mid-to-large enterprise apps.
Code Snippets & Examples: AngularJS vs Angular
One of the easiest ways to understand the difference between Angular and AngularJS is to look at how similar tasks are written in both frameworks. The contrast is instantly noticeable. AngularJS relies on controllers and scopes, while modern Angular uses clean, standalone components built with TypeScript.
Below are simple examples that show how each framework handles components, templates, and data binding.
Code Snippets & Examples: AngularJS vs Angular
One of the easiest ways to understand the difference between Angular and AngularJS is to look at how similar tasks are written in both frameworks. The contrast is instantly noticeable. AngularJS relies on controllers and scopes, while modern Angular uses clean, standalone components built with TypeScript.
Below are simple examples that show how each framework handles components, templates, and data binding.
AngularJS Example including Controller & Template
In AngularJS, UI behavior is controlled using $scope inside a controller. The template reads variables from that scope:
In Javascript

In HTML

In a nutshell, AngularJS depends heavily on $scope, controllers, and two-way binding, which can become harder to manage as apps grow.
Angular with Modern Standalone Component
Modern Angular replaces controllers with components like self-contained units that handle logic, UI, and styling together. Angular 16+ introduces standalone components, removing the need for NgModules in many cases.

Angular components are cleaner, more maintainable, and TypeScript-powered. They scale far better for modern applications.
Binding Comparison of AngularJS vs Angular
While both frameworks allow binding input values to variables, the syntax differs slightly.
AngularJS Binding

Angular Binding

Angular still supports two-way binding when needed, but its default one-way data flow and improved change detection make apps more predictable and performant.
The Role of the Angular Team
The Angular team plays a central role in the framework’s continued growth and reliability. As the official maintainers, they consistently push updates, performance improvements, and new features that keep Angular aligned with the demands of modern web and mobile development. Whether it’s refining change detection, strengthening TypeScript support, or enhancing mobile-ready capabilities, every release reflects their commitment to long-term stability.
Beyond the technical groundwork, the Angular team contributes heavily to the developer ecosystem. With detailed documentation, educational resources, sample projects, and active community support, they make it easier for teams to adopt Angular confidently, even for complex, large-scale applications.
Their emphasis on unit testing, structured architecture, and performance best practices ensures that Angular remains a dependable choice for building scalable digital products. This strong foundation is one reason businesses often look to hire Angular developers who understand the framework deeply and can leverage its ecosystem effectively.
By maintaining a high standard and fostering a vibrant community, the Angular team empowers developers to deliver fast, secure, and future-ready applications across industries.
Conclusion: What’s the Right Choice in the Angular vs AngularJS Debate?
Choosing between Angular and AngularJS comes down to where your product is today and where you want it to go. Modern Angular is faster, more secure, and built for long-term scalability, which is why it powers thousands of enterprise applications across the globe. Meanwhile, AngularJS still serves teams maintaining older codebases or running lightweight apps where a full migration isn’t immediately practical.
Here’s a quick recommendation based on your needs:
- Startups & product teams: Go with Angular. It offers better performance, TypeScript support, cleaner architecture, and long-term stability, exactly what you need to scale confidently.
- Enterprises building large, complex systems: Angular is the clear winner. Its modular structure, tooling, testing ecosystem, and security updates make it far more reliable for mission-critical applications.
- Legacy-app maintainers still on AngularJS: You don’t need to rewrite everything at once. But migration planning should start early so your app stays secure, maintainable, and future-proof. Incremental upgrades or hybrid approaches can ease the transition.
If you need support modernizing an existing app or building a new one, partnering with an experienced angular development company can help you avoid common pitfalls and speed up development.
The Role of the Angular Team
The Angular team is at the heart of the ongoing success and evolution of the Angular framework. As the official maintainers, they are dedicated to ensuring that Angular applications remain at the forefront of modern web development. Their commitment is evident in the regular release of updates, patches, and new features that enhance data binding, improve performance, and expand mobile support for both web and mobile applications.
Beyond technical updates, the Angular team provides a wealth of resources for developers, including comprehensive documentation, tutorials, and active community forums. This extensive support network empowers developers to confidently build and maintain large scale applications, knowing they have access to expert guidance and troubleshooting.
The team’s focus on unit testing, improved data binding, and mobile support ensures that Angular remains a robust framework for developing both mobile and web applications. By fostering a vibrant community and maintaining a high standard for the framework, the Angular team enables developers to deliver performant, reliable, and scalable solutions for a wide range of web development needs.
Conclusion
The above comparison between Angular and AngularJS (Angular vs AngularJS) states the valuable concepts and functionality of both versions. While Angular is used to develop bigger and small applications, Angular.JS is a robust framework used to develop scalable client-side website applications with less development effort and time.
Get in touch with our dedicated angular experts to learn more about how your business can achieve remarkable growth from our Angular and AngularJS development services. Just contact us and discuss your requirements for free.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ's)
Yes, Angular is generally considered better than AngularJS due to its improved performance, better tooling support, improved dependency injection system, and better support for mobile development. However, Angular has a steeper learning curve than AngularJS due to its more complex architecture and use of TypeScript. Ultimately, the choice between Angular and AngularJS depends on the specific needs and requirements of the project.
Angular is a robust web framework that helps with client-side or front-end development. It supports the TypeScript programming language that developers can employ to design the user interface of applications.
No, you don't necessarily need to learn AngularJS before learning Angular. Angular is a complete rewrite of AngularJS, with a different architecture and syntax, so learning AngularJS is not a prerequisite. However, having some experience with JavaScript and web development in general can be helpful when learning Angular.
Both Angular and Angular JS frameworks have substantial benefits, but one can leverage more advantages with the latest version.